Your Complete Guide to Strength, Function, and Injury Prevention
Ever noticed those muscles on the outside of your hips that help you move your legs away from your body’s midline? Those are your abductor muscles, and they play a crucial role in everything from walking and running to maintaining proper posture and balance. Whether you’re an athlete looking to enhance your performance or someone interested in improving their overall fitness, understanding these essential muscles can make a significant difference in your training approach.
Understanding Abductor Muscle Function: More Than Just Hip Movement
The abductor muscles, primarily located on the outer side of your hips and thighs, serve several vital functions in human movement and stability. The main muscles in this group include the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae (TFL). While their primary function is to move your leg away from your body’s centerline (abduction), these muscles do much more than that.
First and foremost, abductor muscles are crucial for maintaining pelvic stability during single-leg activities. When you’re walking or running, these muscles work constantly to keep your pelvis level and prevent it from dropping to the opposite side. This stabilizing action is essential for proper gait mechanics and helps prevent various movement-related issues.
Additionally, your abductor muscles play a significant role in:
- Supporting lateral movements in sports and daily activities
- Maintaining proper knee alignment during squats and lunges
- Protecting your hip joint from excessive stress
- Contributing to proper posture and spine alignment
The often-overlooked nature of these muscles makes them particularly important to address in any well-rounded fitness routine. Their proper functioning can mean the difference between fluid, pain-free movement and potential injury or instability.
The Science Behind Abductor Muscle Activation
Understanding how abductor muscles work on a biomechanical level can help you appreciate their importance. These muscles operate in what’s called the frontal plane of motion, which involves side-to-side movements. During activities like walking or running, your abductors work eccentrically (lengthening under tension) to control the lowering of your hip when your opposite foot leaves the ground.
Research has shown that weak abductor muscles can lead to various compensatory movements, potentially causing:
- Increased stress on the knee joint
- Lower back pain
- Altered running mechanics
- Increased risk of ankle injuries
- Hip impingement issues
Essential Exercises to Strengthen Your Abductor Muscles
Developing strong abductor muscles requires a targeted approach with specific exercises. Here are some of the most effective movements to incorporate into your workout routine:
1. Side-Lying Hip Abductions
This classic exercise directly targets the abductor muscles and is perfect for beginners:
- Lie on your side with legs stacked
- Keep your bottom leg slightly bent for stability
- Lift your top leg straight up while keeping your toe pointed slightly downward
- Perform 3 sets of 12-15 repetitions on each side
For advanced variations:
- Add ankle weights for increased resistance
- Perform pulses at the top of the movement
- Include holds at different angles during the lift
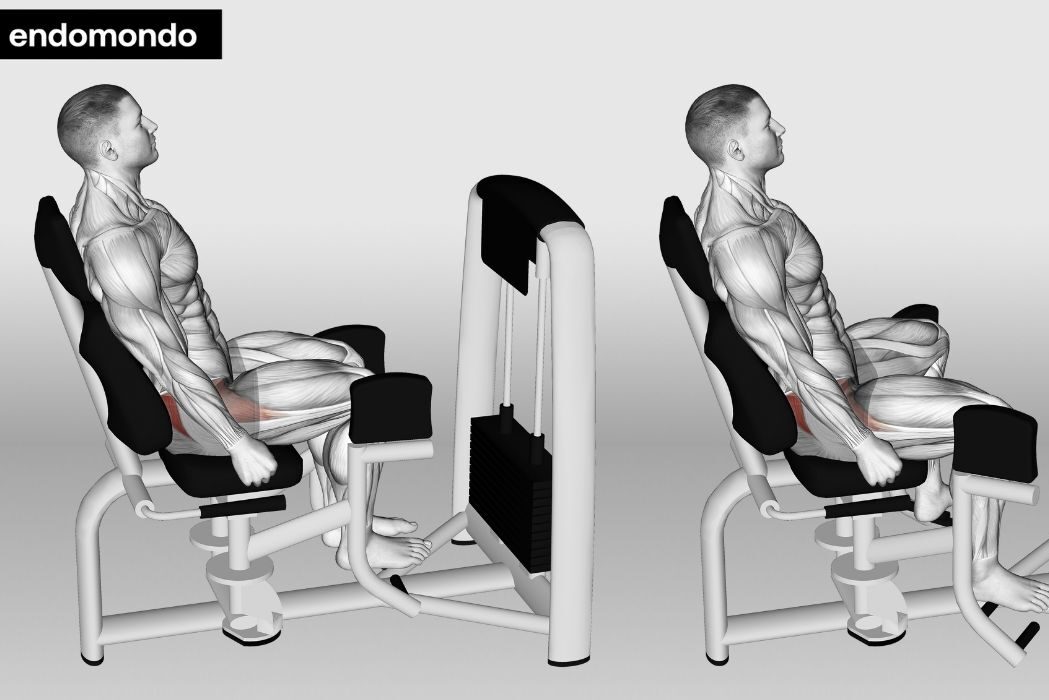
2. Hip Abductor Machine
This gym equipment provides consistent resistance throughout the movement:
- Sit in the machine with your thighs against the pads
- Adjust the weight to a challenging but manageable level
- Keep your back straight and core engaged
- Press your legs outward against the pads
- Control the return movement
- Perform 3 sets of 12-15 repetitions
Pro tips for machine use:
- Focus on slow, controlled movements
- Avoid using momentum
- Keep your feet pointed straight ahead
- Adjust the seat position so your knees align with the pivot point
3. Standing Cable Hip Abductions
For those with access to gym equipment:
- Stand beside a cable machine with the ankle attachment
- Keep your core engaged and maintain an upright posture
- Slowly move your leg outward against the resistance
- Perform 3 sets of 12-15 reps on each leg
4. Lateral Band Walks
A functional exercise that targets the abductors while improving stability:
- Place a resistance band around your thighs, just above your knees
- Maintain a slight squat position
- Step sideways while keeping tension on the band
- Perform 2-3 sets of 15-20 steps in each direction
Progressive Training Techniques
To maximize your results, consider implementing these advanced training principles:
- Progressive Overload
- Gradually increase resistance over time
- Add sets or repetitions systematically
- Incorporate more challenging variations
- Tempo Training
- Slow down the eccentric (lowering) phase
- Include isometric holds at various points
- Vary movement speed for different training effects
- Compound Movement Integration
- Include single-leg squats
- Practice lateral lunges
- Incorporate step-ups with lateral elements
Preventing Abductor Muscle Injuries: Essential Tips and Strategies
Abductor muscle injuries can be particularly frustrating, as they affect many daily activities and can take considerable time to heal. Understanding how to prevent these injuries is crucial for maintaining an active lifestyle and achieving your fitness goals.
Proper Warm-up Techniques
Before any physical activity, especially those involving lateral movements, ensure proper muscle activation:
- Perform dynamic stretches focusing on hip mobility
- Include activation exercises like mini band walks
- Gradually increase the intensity of your warm-up movements
- Pay special attention to warming up the entire hip complex
Common Risk Factors to Address
Several factors can increase your risk of abductor muscle injuries:
- Muscle imbalances between abductors and adductors
- Poor core stability
- Inadequate recovery between workouts
- Sudden increases in training intensity
To minimize these risks, focus on:
- Maintaining balanced strength between inner and outer thigh muscles
- Incorporating regular core strengthening exercises
- Following a progressive training program
- Allowing adequate rest between intense workouts
Recovery and Maintenance
Proper recovery is essential for preventing abductor muscle injuries:
- Use foam rolling techniques on your outer thighs and hips
- Practice gentle stretching after workouts
- Listen to your body and adjust training intensity as needed
- Consider regular massage or mobility work
Long-term Care and Maintenance
To ensure long-term health of your abductor muscles, consider implementing these additional strategies:
- Regular Assessment
- Perform monthly strength tests
- Check for muscle imbalances
- Monitor flexibility and range of motion
- Track progress and adjust training accordingly
- Lifestyle Considerations
- Maintain good posture throughout the day
- Use proper ergonomics at work
- Wear appropriate footwear
- Stay active with varied movement patterns
- Complementary Activities
- Practice yoga for improved flexibility
- Include swimming for low-impact conditioning
- Try Pilates for core and hip stability
- Engage in balance training exercises
By implementing these preventive measures and maintenance strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of abductor muscle injuries while improving your overall movement quality and athletic performance.
Remember that strong, well-functioning abductor muscles contribute significantly to your overall movement quality and athletic performance. Whether you’re an athlete looking to improve performance or someone interested in maintaining good hip health, paying attention to these often-overlooked muscles can make a substantial difference in your fitness journey. Start incorporating these exercises and prevention strategies into your routine, and you’ll likely notice improvements in your stability, strength, and overall movement quality.
With consistent attention to proper training, recovery, and maintenance, you can develop and maintain strong, healthy abductor muscles that will serve you well in both athletic pursuits and daily activities. Remember to progress gradually and listen to your body as you implement these training and prevention strategies.
Be sure to check out our blog posts for more guides on muscles similar to the abductor muscles!